What’s Natural?
By Jim Steele
Extreme scientists and politicians warn we will suffer catastrophic climate change if the earth’s average temperature rises 2.7°F above the Little Ice Age average. They claim we are in a climate crisis because average temperature has already warmed by 1.5°F since 1850 AD. Guided by climate fear, politicians fund whacky engineering schemes to shade the earth with mirrors or aerosols to lower temperatures. But the cooler Little Ice Age endured a much more disastrous climate.
The Little Ice Age coincides with the pre-industrial period. The Little Ice Age spanned a period from 1300 AD to 1850 AD, but the exact timing varies. It was a time of great droughts, retreating tree lines, and agricultural failures leading to massive global famines and rampant epidemics. Meanwhile advancing glaciers demolished European villages and farms and extensive sea ice blocked harbors and prevented trade.
Dr. Michael Mann who preaches dire predictions wrought by global warming described the Little Ice Age as a period of widespread “famine, disease, and increased child mortality in Europe during the 17th–19th century, probably related, at least in part, to colder temperatures and altered weather conditions.” In contrast to current models suggesting global warming will cause wild weather swings, Mann concluded “the Little Ice Age may have been more significant in terms of increased variability of the climate”. Indeed, historical documents from the Little Ice Age describe wild climate swings with extremely cold winters followed by very warm summers, and cold wet years followed by cold dry years.
A series of Little Ice Age droughts lasting several decades devastated Asia between the mid 1300s and 1400s. Resulting famines caused significant societal upheaval within India, China, Sri Lanka, and Cambodia. Bad weather resulted in the Great Famine of 1315-1317 which decimated Europe causing extreme levels of crime, disease, mass death, cannibalism and infanticide. The North American tree-ring data reveal megadroughts lasting several decades during the cool 1500s. The Victorian Great Drought from 1876 to 1878 brought great suffering across much of the tropics with India devastated the most. More than 30 million people are thought to have died at this time from famine worldwide.
The Little Ice Age droughts and famines forced great societal upheaval, and the resulting climate change refugees were forced to seek better lands. But those movements also spread horrendous epidemics. Wild climate swings brought cold and dry weather to central Asia. That forced the Mongols to search for better grazing. As they invaded new territories they spread the Bubonic plague which had devastated parts of Asia earlier. In the 1300s the Mongols passed the plague to Italian merchant ships who then brought it to Europe where it quickly killed one third of Europe’s population. European explorers looking for new trade routes brought smallpox to the Americas, causing small native tribes to go extinct and decimating 25% to 50% of larger tribes. Introduced diseases rapidly reduced Mexico’s population from 30 million to 3 million.
By the 1700s a new killer began to dominate – accidental hypothermia. When indoor temperatures fall below 48°F for prolonged periods, the human body struggles to keep warm, setting off a series of reactions that causes stress and can result in heart attacks. As recently as the 1960s in Great Britain, 20,000 elderly and malnourished people who lacked central heating died from accidental hypothermia. As people with poor heating faced bouts of extreme cold in the 1700s, accidental hypothermia was rampant.
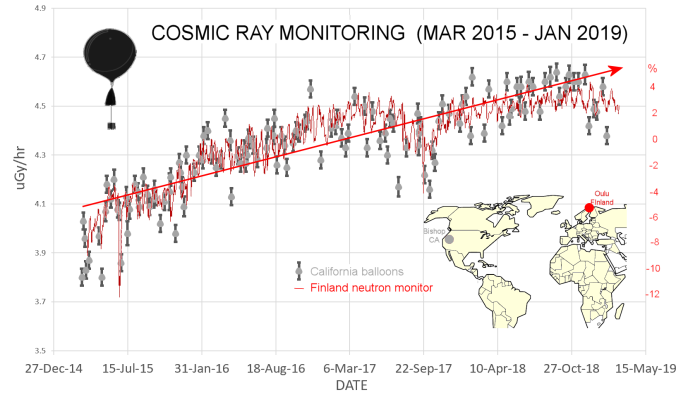
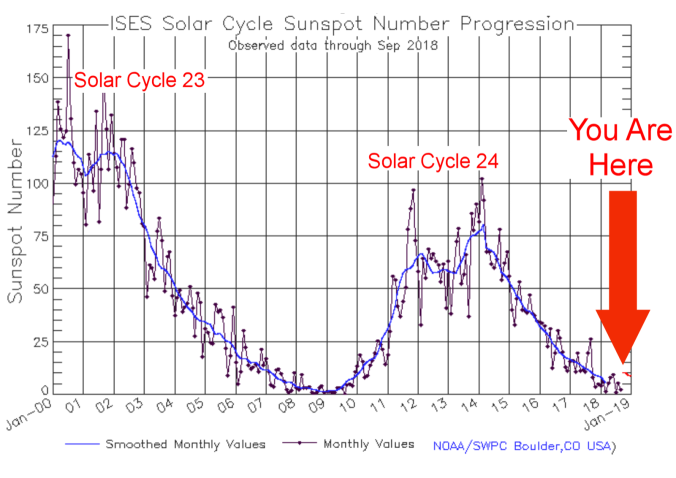
What caused the tragic climate changes of the Little Ice Age? Some scientists suggest lower solar output associated with periods of fewer sunspots. Increasing solar output then reversed the cooling and warmed the 20th century world. As solar output is now falling to the lows of the Little Ice Age, a natural experiment is now in progress testing that solar theory. However other scientists suggest it was rising CO2 that delivered the world from the Little Ice Age.
Increasing CO2 also has a beneficial fertilization effect that is greening the earth. The 20th century warming, whether natural or driven by rising CO2 concentrations, has lengthened the growing season. Famines are being eliminated. Tree-lines stopped retreating and trees are now reclaiming territory lost over the past 500 years. So why is it that now we face a climate crisis?
At the end of the 1300’s Great Famine and the Bubonic Plague epidemic, the earth sustained 350 million people. With today’s advances in technology and milder growing conditions, record high crop yields are now feeding a human population that ballooned to over 7.6 billion.
H/T to WUWT
The open question is: Will our technology save us from the next grand minimum and little ice age? Your thoughts?










In a guess post at Watts Up With That on the cooling signals embedded in the Aurora Borealis, Dr Tim Ball concludes:
This is an interesting analysis of historical documents. Read the full story HERE.
In the comments Leif Svalgaard offered this:
Looking forward to your comments on the questions: Is the auroral evidence of the next grand minimum and a little ice age?